infinite integrals
(0.003 seconds)
21—30 of 72 matching pages
21: 36.9 Integral Identities
…
►For these results and also integrals over doubly-infinite intervals see Berry and Wright (1980).
…
22: 1.15 Summability Methods
23: 19.3 Graphics
…
►
►
►
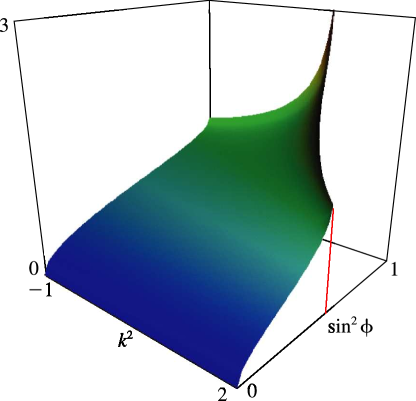
Figure 19.3.3:
as a function of and for , .
If (), then the function reduces to , becoming infinite when .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
►
►
►
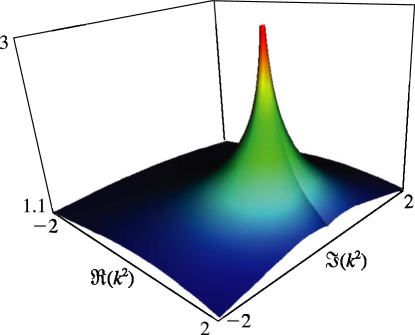
Figure 19.3.9:
as a function of complex for , .
…On the branch cut () it is infinite at , and has the value when .
Magnify
3D
Help
…
24: 25.12 Polylogarithms
…
►
25.12.9
…
25: 27.12 Asymptotic Formulas: Primes
26: 19.5 Maclaurin and Related Expansions
27: 13.16 Integral Representations
…
►
13.16.2
,
…
28: 5.17 Barnes’ -Function (Double Gamma Function)
29: 7.13 Zeros
…
►In the first quadrant of
has an infinite set of zeros , , arranged in order of increasing absolute value.
…