18 Orthogonal PolynomialsAskey Scheme18.20 Hahn Class: Explicit Representations18.22 Hahn Class: Recurrence Relations and
Differences
§18.21 Hahn Class: Interrelations
Contents
§18.21(i) Dualities
Duality of Hahn and Dual Hahn
| 18.21.1 | |||
| . | |||
For the dual Hahn polynomial see §18.25.
Self-Dualities
| 18.21.2 | ||||
| . | ||||
| . | ||||
| . | ||||
§18.21(ii) Limit Relations and Special Cases
Hahn Krawtchouk
| 18.21.3 | |||
Hahn Meixner
| 18.21.4 | |||
Hahn Jacobi
| 18.21.5 | |||
Krawtchouk Charlier
| 18.21.6 | |||
Meixner Charlier
| 18.21.7 | |||
Meixner Laguerre
| 18.21.8 | |||
Charlier Hermite
| 18.21.9 | |||
Continuous Hahn Meixner–Pollaczek
| 18.21.10 | |||
| 18.21.11 | |||
Meixner–Pollaczek Laguerre
| 18.21.12 | |||
Meixner–Pollaczek Hermite
| 18.21.13 | |||
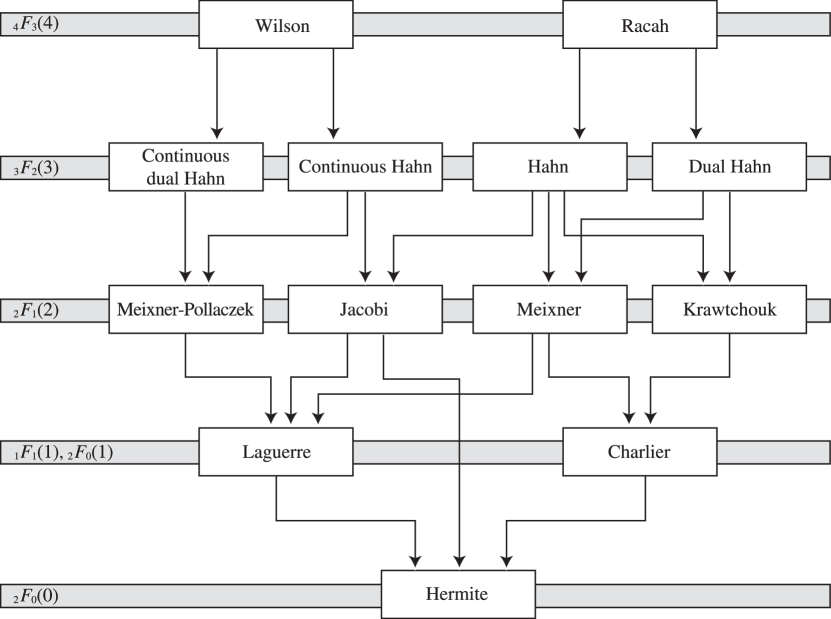
A graphical representation of limits in §§18.7(iii), 18.21(ii), and 18.26(ii) is provided by the Askey scheme depicted in Figure 18.21.1.