kernel functions
(0.004 seconds)
1—10 of 33 matching pages
1: 10.62 Graphs
§10.62 Graphs
►For the modulus functions and see §10.68(i) with . … ►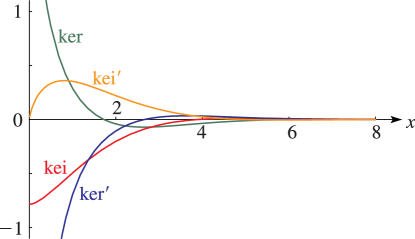 ►
►
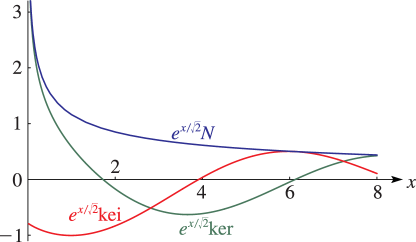 ►
►
2: 10.61 Definitions and Basic Properties
3: 10.70 Zeros
§10.70 Zeros
… ►
10.70.1
…
►
,
…
►In the case , numerical tabulations (Abramowitz and Stegun (1964, Table 9.12)) indicate that each of (10.70.2) corresponds to the th zero of the function on the left-hand side.
…
4: 31.10 Integral Equations and Representations
…
►
Kernel Functions
… ►
31.10.9
…
►Fuchs–Frobenius solutions are represented in terms of Heun functions
by (31.10.1) with , , and with kernel chosen from
…
►
Kernel Functions
… ►
31.10.19
…
5: 10.67 Asymptotic Expansions for Large Argument
6: 10.63 Recurrence Relations and Derivatives
7: 10.69 Uniform Asymptotic Expansions for Large Order
8: 28.10 Integral Equations
…
►
§28.10(i) Equations with Elementary Kernels
… ►§28.10(ii) Equations with Bessel-Function Kernels
…9: 10.68 Modulus and Phase Functions
…
►
10.68.2
…
10: 10.65 Power Series
…
►
10.65.3
…
