.2021世界杯投注_『welcom_』世界杯挣钱机遇_w6n2c9o_2022年12月2日21时22分29秒_f7zjzd5rf_gov_hk
(0.007 seconds)
11—20 of 818 matching pages
11: 26.2 Basic Definitions
…
►Thus is the permutation , , .
…
►Here , and .
…
►A lattice path is a directed path on the plane integer lattice .
…
►As an example, , , is a partition of .
…
►As an example, is a partition of 13.
…
12: 26.21 Tables
…
►Andrews (1976) contains tables of the number of unrestricted partitions, partitions into odd parts, partitions into parts , partitions into parts , and unrestricted plane partitions up to 100.
It also contains a table of Gaussian polynomials up to .
…
13: 28.16 Asymptotic Expansions for Large
14: Publications
…
►
D. W. Lozier, B. R. Miller and B. V. Saunders (1999)
Design of a Digital Mathematical Library for Science, Technology and Education,
Proceedings of the
IEEE Forum on Research and Technology Advances in Digital Libraries (IEEE ADL ’99,
Baltimore, Maryland, May 19, 1999).

…
►
Q. Wang and B. V. Saunders (2005)
Web-Based 3D Visualization in a Digital Library of Mathematical Functions,
Proceedings of the Web3D Symposium,
Bangor, UK, March 29–April 1, 2005.

►
B. V. Saunders and Q. Wang (2006)
From B-Spline Mesh Generation to Effective Visualizations for the
NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions,
in Curve and Surface Design, Proceedings of the Sixth International
Conference on Curves and Surfaces,
Avignon, France June 29–July 5, 2006,
pp. 235–243.

…
►
B. I. Schneider, B. R. Miller and B. V. Saunders (2018)
NIST’s Digital Library of Mathematial Functions,
Physics Today
71, 2, 48 (2018), pp. 48–53.

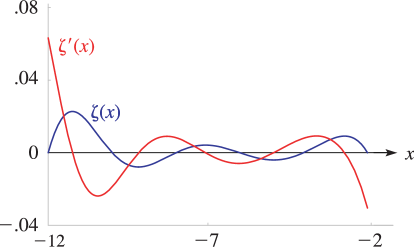
15: 5.17 Barnes’ -Function (Double Gamma Function)
…
►
5.17.2
.
►
5.17.3
…
►
5.17.5
…
►Here is the Bernoulli number (§24.2(i)), and is Glaisher’s constant, given by
…
►
5.17.7
…
16: 26.4 Lattice Paths: Multinomial Coefficients and Set Partitions
…
►For
…
►
is the number of permutations of with cycles of length 1, cycles of length 2, , and cycles of length :
… is the number of set partitions of with subsets of size 1, subsets of size 2, , and subsets of size :
…For each all possible values of are covered.
…
►where the summation is over all nonnegative integers such that .
…
17: 28.6 Expansions for Small
…
►For more details on these expansions and recurrence relations for the coefficients see Frenkel and Portugal (2001, §2).
►The coefficients of the power series of , and also , are the same until the terms in and , respectively.
…
►Here for , for , and for and .
…
►where is the unique root of the equation in the interval , and .
…
►For more details on these expansions and recurrence relations for the coefficients see Frenkel and Portugal (2001, §2).
…
18: 3.4 Differentiation
…
►If is continuous on the interval defined in §3.3(i), then the remainder in (3.4.1) is given by
…
►
►
…
►With the choice (which is crucial when is large because of numerical cancellation) the integrand equals at the dominant points , and in combination with the factor in front of the integral sign this gives a rough approximation to .
…
►For additional formulas involving values of and on square, triangular, and cubic grids, see Collatz (1960, Table VI, pp. 542–546).
…
19: Bibliography G
…
►
Algorithm 471: Exponential integrals.
Comm. ACM 16 (12), pp. 761–763.
…
►
Mémoire sur les fonctions hypergéométriques d’ordre supérieur.
Ann. Sci. École Norm. Sup. (2) 12, pp. 261–286, 395–430 (French).
…
►
The solutions of Painlevé’s fifth equation.
Differ. Uravn. 12 (4), pp. 740–742 (Russian).
►
One-parameter systems of solutions of Painlevé equations.
Differ. Uravn. 14 (12), pp. 2131–2135 (Russian).
…
►
Algorithm 300: Coulomb wave functions.
Comm. ACM 10 (4), pp. 244–245.
…