Bernoulli%20monosplines
(0.002 seconds)
1—10 of 144 matching pages
1: 24.1 Special Notation
2: 24.17 Mathematical Applications
…
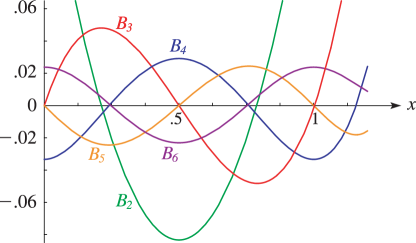
►The functions
…
►
Bernoulli Monosplines
… ► is a monospline of degree , and it follows from (24.4.25) and (24.4.27) that … ► … ►3: 24.2 Definitions and Generating Functions
§24.2 Definitions and Generating Functions
►§24.2(i) Bernoulli Numbers and Polynomials
… ►§24.2(iii) Periodic Bernoulli and Euler Functions
… ► …4: 24.18 Physical Applications
§24.18 Physical Applications
►Bernoulli polynomials appear in statistical physics (Ordóñez and Driebe (1996)), in discussions of Casimir forces (Li et al. (1991)), and in a study of quark-gluon plasma (Meisinger et al. (2002)). …5: 24.20 Tables
§24.20 Tables
… ►Wagstaff (1978) gives complete prime factorizations of and for and , respectively. …6: 24.3 Graphs
7: 25.11 Hurwitz Zeta Function
8: 5.11 Asymptotic Expansions
…
►For the Bernoulli numbers , see §24.2(i).
…
►Wrench (1968) gives exact values of up to .
…
►where is fixed, and is the Bernoulli polynomial defined in §24.2(i).
…
►In terms of generalized Bernoulli polynomials (§24.16(i)), we have for ,
►
5.11.17
…
9: 24.4 Basic Properties
…
►