lemniscatic case
♦
5 matching pages ♦
(0.001 seconds)
5 matching pages
1: 23.4 Graphics
…
►
► ►
►
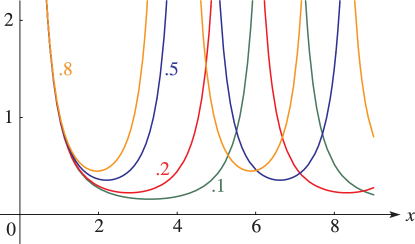
Figure 23.4.1:
for , = 0.
…(Lemniscatic case.)
Magnify
…
►
► ►
►
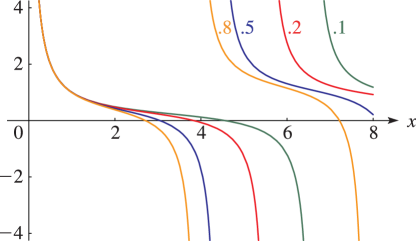
Figure 23.4.3:
for , = 0.
…(Lemniscatic case.)
Magnify
…
►
► ►
►
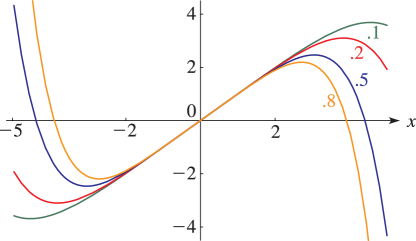
Figure 23.4.5:
for , = 0.
…(Lemniscatic case.)
Magnify
…
►
► ►
►
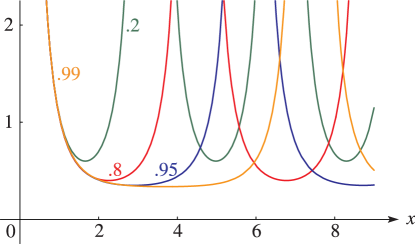
Figure 23.4.7:
with , for , = 0.
…(Lemniscatic case.)
Magnify
…
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
2: 23.5 Special Lattices
…
►
§23.5(iii) Lemniscatic Lattice
… ► and have the same sign unless when both are zero: the pseudo-lemniscatic case. As a function of the root is increasing. …3: 19.20 Special Cases
4: 22.5 Special Values
…
►For values of when (lemniscatic case) see §23.5(iii), and for (equianharmonic case) see §23.5(v).
5: 23.22 Methods of Computation
…
►
(b)
…
If , then
23.22.2
There are 4 possible pairs (, ), corresponding to the 4 rotations of a square lattice. The lemniscatic case occurs when and .
