Askey–Wilson polynomials
(0.005 seconds)
1—10 of 26 matching pages
1: 18.29 Asymptotic Approximations for -Hahn and Askey–Wilson Classes
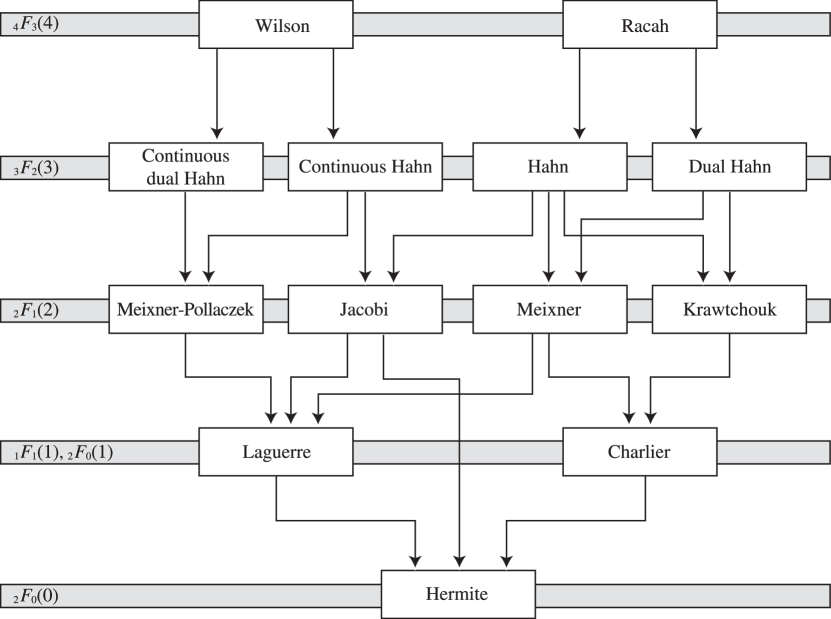
§18.29 Asymptotic Approximations for -Hahn and Askey–Wilson Classes
►Ismail (1986) gives asymptotic expansions as , with and other parameters fixed, for continuous -ultraspherical, big and little -Jacobi, and Askey–Wilson polynomials. …For Askey–Wilson the leading term is given by …2: 18.28 Askey–Wilson Class
…
►
§18.28(ii) Askey–Wilson Polynomials
… ►The polynomials are symmetric in the parameters . … ►Recurrence Relation
… ►Duality
… ►
18.28.29
…
3: 18.1 Notation
…
►
…
Askey–Wilson: .
4: Tom H. Koornwinder
…
►Koornwinder has published numerous papers on special functions, harmonic analysis, Lie groups, quantum groups, computer algebra, and their interrelations, including an interpretation of Askey–Wilson polynomials on quantum SU(2), and a five-parameter extension (the Macdonald–Koornwinder polynomials) of Macdonald’s polynomials for root systems BC.
…
5: Richard A. Askey
6: 18.38 Mathematical Applications
…
►If we consider this abstract algebra with additional relation (18.38.9) and with dependence on according to (18.38.7) then it is isomorphic with the algebra generated by given by (18.28.6_2), and given by (18.38.4), and act on the linear span of the Askey–Wilson polynomials (18.28.1).
See Zhedanov (1991), Granovskiĭ et al. (1992, §3), Koornwinder (2007a, §2) and Terwilliger (2011).
…
►The Dunkl type operator is a -difference-reflection operator acting on Laurent polynomials and its eigenfunctions, the nonsymmetric Askey–Wilson polynomials, are linear combinations of the symmetric Laurent polynomial
and the ‘anti-symmetric’ Laurent polynomial
, where is given in (18.28.1_5).
…
►Dunkl type operators and nonsymmetric polynomials have been associated with various other families in the Askey scheme and -Askey scheme, in particular with Wilson polynomials, see Groenevelt (2007), and with Jacobi polynomials, see Koornwinder and Bouzeffour (2011, §7).
…
7: Bibliography K
…
►
Nonsymmetric Askey-Wilson polynomials as vector-valued polynomials.
Appl. Anal. 90 (3-4), pp. 731–746.
…
►
Askey-Wilson Polynomials for Root Systems of Type
.
In Hypergeometric Functions on Domains of Positivity, Jack
Polynomials, and Applications (Tampa, FL, 1991),
Contemp. Math., Vol. 138, pp. 189–204.
►
Askey-Wilson polynomials as zonal spherical functions on the quantum group.
SIAM J. Math. Anal. 24 (3), pp. 795–813.
…
►
The structure relation for Askey-Wilson polynomials.
J. Comput. Appl. Math. 207 (2), pp. 214–226.
…
►
Askey-Wilson polynomial.
Scholarpedia 7 (7), pp. 7761.
…
8: Bibliography Z
…
►
“Hidden symmetry” of Askey-Wilson polynomials.
Theoret. and Math. Phys. 89 (2), pp. 1146–1157.
…
9: Errata
…
►
Equation (18.28.1)
…
18.28.1
18.28.1_5
Previously we presented all the information of these formulas in one equation