hyperbolic%20umbilic%20bifurcation%20set
(0.003 seconds)
11—20 of 631 matching pages
11: 36.10 Differential Equations
12: 36.11 Leading-Order Asymptotics
§36.11 Leading-Order Asymptotics
… ►and far from the bifurcation set, the cuspoid canonical integrals are approximated by … ►13: 36.7 Zeros
§36.7(iii) Elliptic Umbilic Canonical Integral
… ►The zeros are lines in space where is undetermined. …Near , and for small and , the modulus has the symmetry of a lattice with a rhombohedral unit cell that has a mirror plane and an inverse threefold axis whose and repeat distances are given by … ►§36.7(iv) Swallowtail and Hyperbolic Umbilic Canonical Integrals
►The zeros of these functions are curves in space; see Nye (2007) for and Nye (2006) for .14: 4.40 Integrals
§4.40 Integrals
… ►§4.40(ii) Indefinite Integrals
… ►§4.40(iii) Definite Integrals
… ►§4.40(iv) Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
… ►Extensive compendia of indefinite and definite integrals of hyperbolic functions include Apelblat (1983, pp. 96–109), Bierens de Haan (1939), Gröbner and Hofreiter (1949, pp. 139–160), Gröbner and Hofreiter (1950, pp. 160–167), Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (2000, Chapters 2–4), and Prudnikov et al. (1986a, §§1.4, 1.8, 2.4, 2.8).15: Bibliography B
16: 36.9 Integral Identities
17: 36.8 Convergent Series Expansions
18: Bibliography N
19: 4.30 Elementary Properties
20: Errata
Scales were corrected in all figures. The interval was replaced by and replaced by . All plots and interactive visualizations were regenerated to improve image quality.
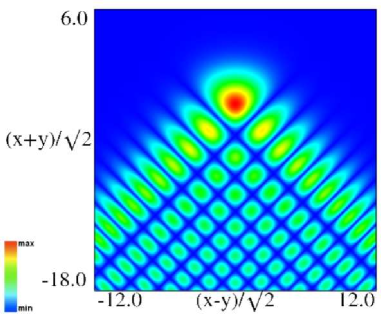 |
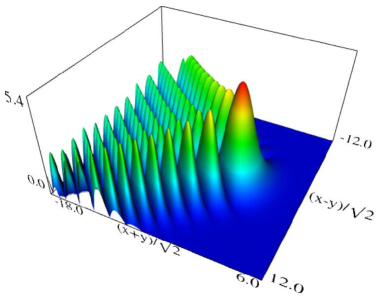 |
| (a) Density plot. | (b) 3D plot. |
Figure 36.3.9: Modulus of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral function .
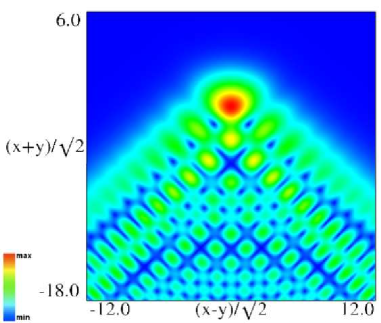 |
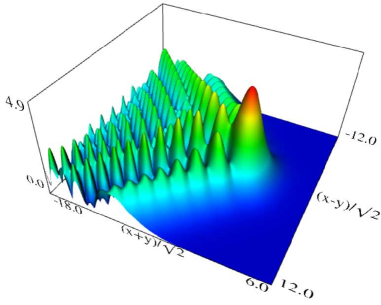 |
| (a) Density plot. | (b) 3D plot. |
Figure 36.3.10: Modulus of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral function .
 |
 |
| (a) Density plot. | (b) 3D plot. |
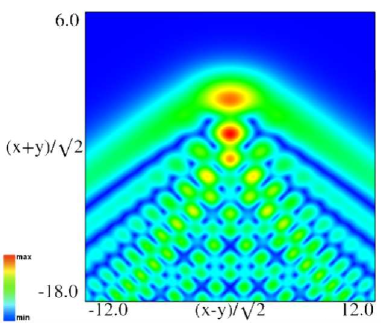
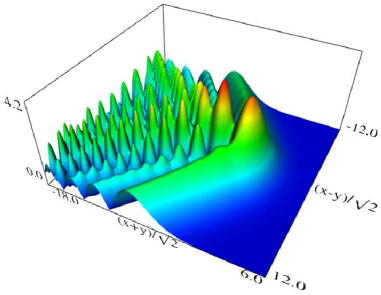
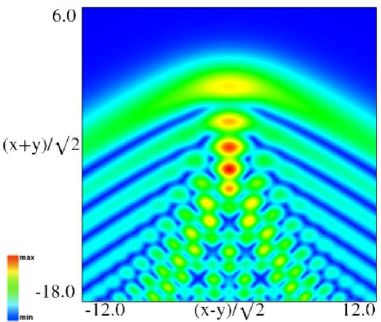
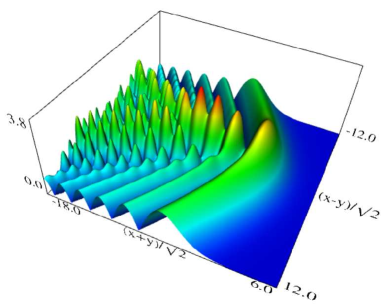
Figure 36.3.11: Modulus of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral function .
 |
 |
| (a) Density plot. | (b) 3D plot. |
Figure 36.3.12: Modulus of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral function .
Reported 2016-09-12 by Dan Piponi.
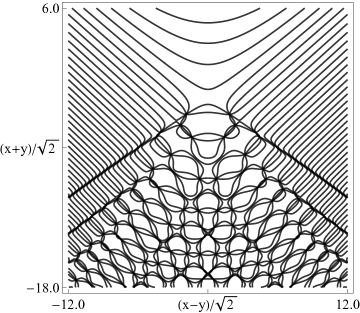
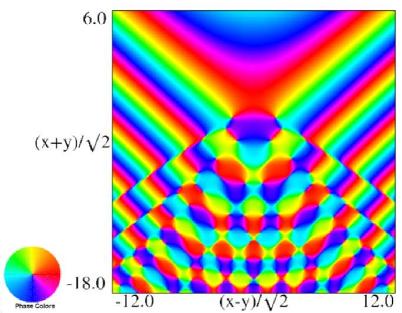
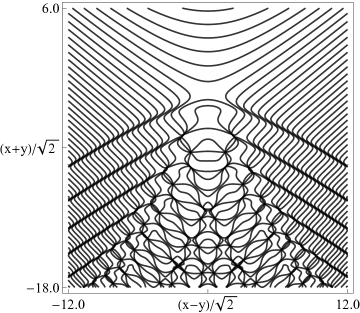
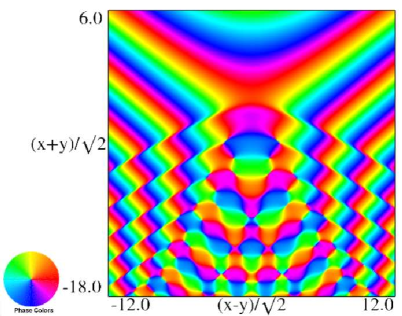
The scaling error reported on 2016-09-12 by Dan Piponi also applied to contour and density plots for the phase of the hyperbolic umbilic canonical integrals. Scales were corrected in all figures. The interval was replaced by and replaced by . All plots and interactive visualizations were regenerated to improve image quality.
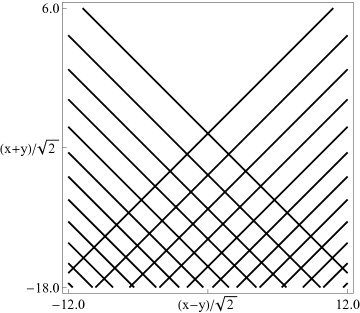 |
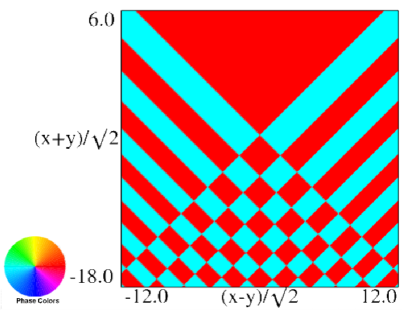 |
| (a) Contour plot. | (b) Density plot. |
Figure 36.3.18: Phase of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral .
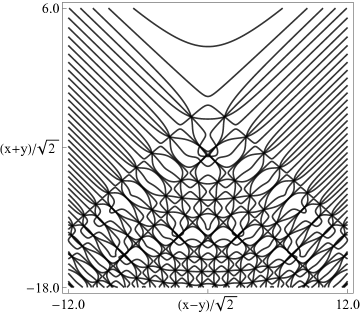 |
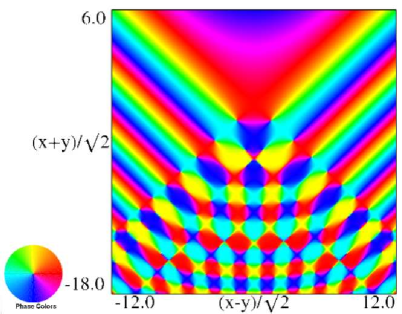 |
| (a) Contour plot. | (b) Density plot. |
Figure 36.3.19: Phase of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral .
 |
 |
| (a) Contour plot. | (b) Density plot. |
Figure 36.3.20: Phase of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral .
 |
 |
| (a) Contour plot. | (b) Density plot. |
Figure 36.3.21: Phase of hyperbolic umbilic canonical integral .
Reported 2016-09-28.
Originally this equation appeared with in the second term, rather than .
Reported 2010-04-02.
