7 Error Functions, Dawson’s and Fresnel IntegralsProperties7.18 Repeated Integrals of the Complementary Error Function7.20 Mathematical Applications
§7.19 Voigt Functions
Contents
- §7.19(i) Definitions
- §7.19(ii) Graphics
- §7.19(iii) Properties
- §7.19(iv) Other Integral Representations
§7.19(i) Definitions
For and ,
| 7.19.1 | |||
| 7.19.2 | |||
| 7.19.3 | |||
| . | |||
| 7.19.4 | |||
is sometimes called the line broadening function; see, for example, Finn and Mugglestone (1965).
§7.19(ii) Graphics
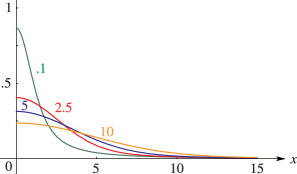
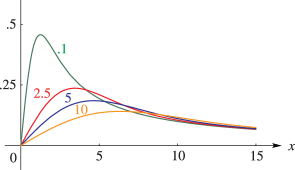
§7.19(iii) Properties
| 7.19.5 | ||||
| 7.19.6 | ||||
| 7.19.7 | ||||
| 7.19.8 | ||||
| 7.19.9 | ||||
§7.19(iv) Other Integral Representations
| 7.19.10 | |||
| 7.19.11 | |||
