modulus and phase
(0.002 seconds)
11—20 of 134 matching pages
11: 33.2 Definitions and Basic Properties
…
►
33.2.7
…
ⓘ
- Defines:
- : irregular Coulomb radial functions
- Symbols:
- : Coulomb phase shift, : Whittaker confluent hypergeometric function, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : imaginary unit, : nonnegative integer, : nonnegative real variable and : real parameter
- Referenced by:
- §13.18(vi), §33.23(vi)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/33.2.E7
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §33.2(iii), §33.2 and Ch.33
12: 9.5 Integral Representations
…
►
9.5.7
.
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : cosine function, : differential of , : exponential function, : base of natural logarithm, : integral, : phase, : complex variable and : change of variable
- Source:
- Copson (1963, (2.1))
- Referenced by:
- §9.5(ii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.5.E7
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.5(ii), §9.5 and Ch.9
9.5.8
.
…
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : gamma function, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : differential of , : base of natural logarithm, : integral, : phase, : complex variable and : change of variable
- Proof sketch:
- Follows from (9.6.21) and (13.4.4).
- Referenced by:
- §9.17(iii), §9.5(ii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.5.E8
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.5(ii), §9.5 and Ch.9
13: 11.11 Asymptotic Expansions of Anger–Weber Functions
…
►
11.11.11
, ,
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Pochhammer’s symbol (or shifted factorial), : Anger–Weber function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : real or complex order, : nonnegative integer, : arbitrary small positive constant, : parameter and : expansion function
- Sources:
- Dingle (1973, p. 388); Olver (1997b, pp. 103 and 352)
- Proof sketch:
- Derivable by applying Laplace’s method to the integral (11.10.4).
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.11.E11
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- Clarification (effective with 1.1.2):
-
The constraint which was originally , has been extended
to be , .
Suggested 2021-04-05 by Gergő Nemes
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.11(iii), §11.11 and Ch.11
11.11.15
, .
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Anger–Weber function, : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : real or complex order, : arbitrary small positive constant and : parameter
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, pp. 103 and 352)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.11.E15
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- Clarification (effective with 1.1.2):
-
The constraint has been extended to include .
Suggested 2021-04-06 by Gergő Nemes
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.11(iii), §11.11 and Ch.11
11.11.18
, ,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Anger function, : gamma function, : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : phase, : real or complex order and : arbitrary small positive constant
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, pp. 103 and 352)
- Proof sketch:
- Dervivable using (11.10.15), (11.10.16), (11.11.8), (11.11.10), (11.11.16) and the expansions in Watson (1944, §8.42).
- Referenced by:
- §11.11(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.11.E18
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- Clarification (effective with 1.1.2):
-
The constraint which originally was , has been extended
to be , .
Suggested 2021-04-05 by Gergő Nemes
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.11(iii), §11.11 and Ch.11
11.11.19
, .
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : gamma function, : Weber function, : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : phase, : real or complex order and : arbitrary small positive constant
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, pp. 103 and 352)
- Proof sketch:
- Dervivable using (11.10.15), (11.10.16), (11.11.8), (11.11.10), (11.11.16) and the expansions in Watson (1944, §8.42).
- Referenced by:
- §11.11(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.11.E19
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- Clarification (effective with 1.1.2):
-
The constraint which originally was , has been extended
to be , .
Suggested 2021-04-05 by Gergő Nemes
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.11(iii), §11.11 and Ch.11
14: 10.3 Graphics
…
►
► ►
►
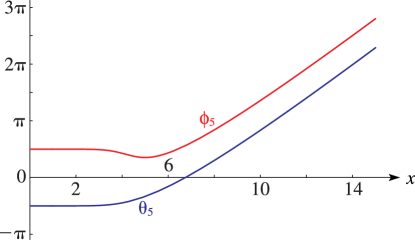
Figure 10.3.4:
, , .
Magnify
…
§10.3(i) Real Order and Variable
►For the modulus and phase functions , , , and see §10.18. … ► ►
►
15: 15.6 Integral Representations
…
►In (15.6.3) the point lies outside the integration contour, the contour cuts the real axis between and , at which point and .
►In (15.6.4) the point lies outside the integration contour, and at the point where the contour cuts the negative real axis and .
…
16: 9.7 Asymptotic Expansions
…
►
9.7.5
,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : nonnegative integer, : complex variable, : small positive constant, : change of variable and : expansion coefficient
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, (1.07), pp. 392 and 413)
- Referenced by:
- (9.10.4), (9.10.6), §9.7(iii), §9.7(iv), §9.7(iv), §9.7(v), Erratum (V1.0.17) for Subsection 9.7(iv)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.7.E5
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.7(ii), §9.7 and Ch.9
9.7.6
,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : nonnegative integer, : complex variable, : small positive constant, : change of variable and : expansion coefficient
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, (1.07), pp. 392 and 413)
- Referenced by:
- §9.7(iii), §9.7(iv), §9.7(iv), §9.7(v), Erratum (V1.0.17) for Subsection 9.7(iv)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.7.E6
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.7(ii), §9.7 and Ch.9
9.7.7
,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : nonnegative integer, : complex variable, : small positive constant, : change of variable and : expansion coefficient
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, (1.16), pp. 393 and 414)
- Referenced by:
- (9.10.5), (9.10.7), §9.7(iii), §9.7(iii), §9.7(iv), §9.7(v), Erratum (V1.0.17) for Subsection 9.7(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.7.E7
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.7(ii), §9.7 and Ch.9
9.7.8
.
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : phase, : nonnegative integer, : complex variable, : small positive constant, : change of variable and : expansion coefficient
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, (1.16), pp. 393 and 414)
- Referenced by:
- §9.7(iii), §9.7(iii), Erratum (V1.0.17) for Subsection 9.7(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.7.E8
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.7(ii), §9.7 and Ch.9
9.7.9
,
…
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Airy function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : cosine function, : phase, : sine function, : nonnegative integer, : complex variable, : small positive constant, : change of variable and : expansion coefficient
- Source:
- Olver (1997b, (1.08), pp. 392 and 413)
- Referenced by:
- §9.7(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/9.7.E9
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §9.7(ii), §9.7 and Ch.9
17: 4.2 Definitions
…
►For see §1.9(i).
…
►For example, with the definition (4.2.5) the identity (4.8.7) is valid only when , but with the closed definition the identity (4.8.7) is valid when .
…
►The general value of the phase is given by
…
►
…where for the principal value of , and is unrestricted in the general case.
…
18: 10.30 Limiting Forms
…
►
10.30.4
,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : modified Bessel function of the first kind, : phase, : complex variable, : complex parameter and : small positive constant
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/10.30.E4
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §10.30(ii), §10.30 and Ch.10
10.30.5
.
…
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : imaginary unit, : modified Bessel function of the first kind, : phase, : complex variable, : complex parameter and : small positive constant
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/10.30.E5
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §10.30(ii), §10.30 and Ch.10
19: 7.7 Integral Representations
…
►
7.7.7
, .
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : complementary error function, : differential of , : base of natural logarithm, : integral, : phase and : real variable
- A&S Ref:
- 7.4.33 (in different form)
- Referenced by:
- §7.7(i), §7.8
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/7.7.E7
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §7.7(i), §7.7 and Ch.7
7.7.8
,
.
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : differential of , : base of natural logarithm, : integral and : phase
- A&S Ref:
- 7.4.3 (in different form)
- Referenced by:
- §7.7(i)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/7.7.E8
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §7.7(i), §7.7 and Ch.7
7.7.10
,
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : auxiliary function for Fresnel integrals, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : differential of , : base of natural logarithm, : integral, : phase and : complex variable
- A&S Ref:
- 7.4.26 (in different form)
- Referenced by:
- §7.12(ii), §7.7(ii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/7.7.E10
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §7.7(ii), §7.7 and Ch.7
7.7.11
,
…
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : auxiliary function for Fresnel integrals, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : differential of , : base of natural logarithm, : integral, : phase and : complex variable
- A&S Ref:
- 7.4.25 (in different form)
- Referenced by:
- §7.12(ii), §7.7(ii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/7.7.E11
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §7.7(ii), §7.7 and Ch.7
20: 11.6 Asymptotic Expansions
…
►
11.6.1
,
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : gamma function, : Struve function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : phase, : complex variable, : real or complex order, : nonnegative integer and : arbitrary small positive constant
- A&S Ref:
- 12.1.29
- Referenced by:
- §11.6(i), §11.6(i), §11.6(i), §11.6(i)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.6.E1
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.6(i), §11.6 and Ch.11
11.6.2
.
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : gamma function, : modified Struve function, : Poincaré asymptotic expansion, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : phase, : complex variable, : real or complex order, : nonnegative integer and : arbitrary small positive constant
- A&S Ref:
- 12.2.6
- Referenced by:
- §11.6(i), §11.6(i), §11.6(i)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.6.E2
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.6(i), §11.6 and Ch.11
11.6.5
.
…
►
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : Struve function, : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : base of natural logarithm, : modified Struve function, : phase, : complex variable, : real or complex order and : arbitrary small positive constant
- Referenced by:
- (11.11.7)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.6.E5
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.6(ii), §11.6 and Ch.11
§11.6(iii) Large , Fixed
… ►
11.6.9
,
…
ⓘ
- Symbols:
- : asymptotic equality, : the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, : modified Bessel function of the first kind, : modified Struve function, : phase, : real or complex order, : arbitrary small positive constant and : parameter
- Referenced by:
- §11.6(iii)
- Permalink:
- http://dlmf.nist.gov/11.6.E9
- Encodings:
- pMML, png, TeX
- See also:
- Annotations for §11.6(iii), §11.6 and Ch.11
