functions s(ϵ,ℓ;r),c(ϵ,ℓ;r)
(0.020 seconds)
31—40 of 570 matching pages
31: 11.1 Special Notation
…
►The functions treated in this chapter are the Struve functions
and , the modified Struve functions
and , the Lommel functions
and , the Anger function
, the Weber function
, and the associated Anger–Weber function
.
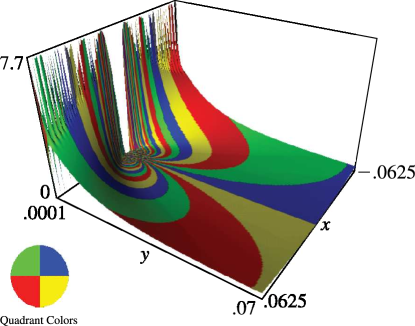
32: 23.16 Graphics
33: 22.1 Special Notation
…
►The functions treated in this chapter are the three principal Jacobian elliptic functions
, , ; the nine subsidiary Jacobian elliptic functions
, , , , , , , , ; the amplitude function
; Jacobi’s epsilon and zeta functions
and .
…
►Other notations for are and with ; see Abramowitz and Stegun (1964) and Walker (1996).
…
34: 13.24 Series
35: 19.10 Relations to Other Functions
…
►
§19.10(i) Theta and Elliptic Functions
►For relations of Legendre’s integrals to theta functions, Jacobian functions, and Weierstrass functions, see §§20.9(i), 22.15(ii), and 23.6(iv), respectively. … ►
19.10.2
36: 13.1 Special Notation
…
►The main functions treated in this chapter are the Kummer functions
and , Olver’s function
, and the Whittaker functions
and .
…
37: 10.1 Special Notation
…
►For older notations see British Association for the Advancement of Science (1937, pp. xix–xx) and Watson (1944, Chapters 1–3).
38: 25.20 Approximations
…
►
•
►
•
…
►
•
Cody et al. (1971) gives rational approximations for in the form of quotients of polynomials or quotients of Chebyshev series. The ranges covered are , , , . Precision is varied, with a maximum of 20S.
Piessens and Branders (1972) gives the coefficients of the Chebyshev-series expansions of and , , for (23D).
39: 25.13 Periodic Zeta Function
…
►The notation is used for the polylogarithm with real:
►
25.13.1
…
►
25.13.2
, ,
►
25.13.3
if ; if .