exponential function
(0.017 seconds)
21—30 of 414 matching pages
21: 8.24 Physical Applications
§8.24 Physical Applications
… ►The function appears in: discussions of power-law relaxation times in complex physical systems (Sornette (1998)); logarithmic oscillations in relaxation times for proteins (Metzler et al. (1999)); Gaussian orbitals and exponential (Slater) orbitals in quantum chemistry (Shavitt (1963), Shavitt and Karplus (1965)); population biology and ecological systems (Camacho et al. (2002)). … ►The function , with , appears in theories of transport and radiative equilibrium (Hopf (1934), Kourganoff (1952), Altaç (1996)). ►With more general values of , supplies fundamental auxiliary functions that are used in the computation of molecular electronic integrals in quantum chemistry (Harris (2002), Shavitt (1963)), and also wave acoustics of overlapping sound beams (Ding (2000)).22: 13.18 Relations to Other Functions
…
►
13.18.3
…
►When is an integer the Whittaker functions can be expressed as incomplete gamma functions (or generalized exponential integrals).
…
►
13.18.4
►
13.18.5
…
►
13.18.6
…
23: 5.6 Inequalities
24: 4.9 Continued Fractions
…
►
§4.9(ii) Exponentials
… ►For other continued fractions involving the exponential function see Lorentzen and Waadeland (1992, pp. 563–564). …25: 18.32 OP’s with Respect to Freud Weights
26: 36.2 Catastrophes and Canonical Integrals
27: 10.56 Generating Functions
…
►
10.56.5
28: 4.8 Identities
29: 10.62 Graphs
§10.62 Graphs
►For the modulus functions and see §10.68(i) with . … ►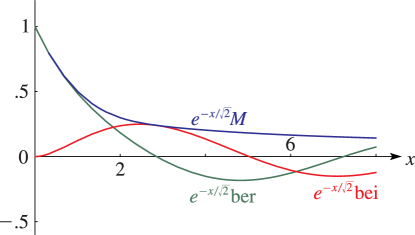 ►
►
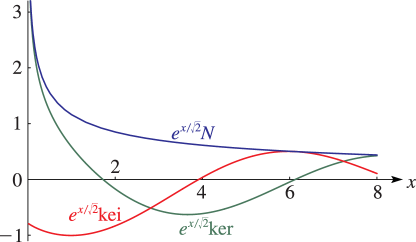 ►
►
