Olver associated Legendre function
(0.014 seconds)
11—20 of 42 matching pages
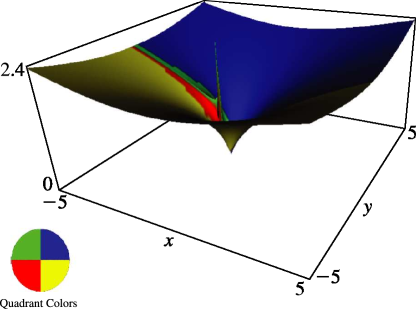
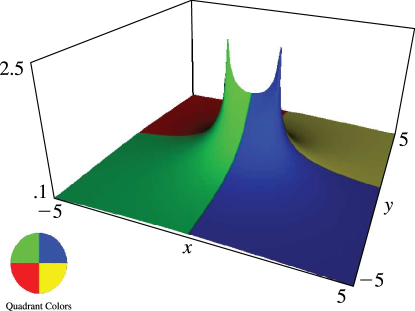
11: 14.22 Graphics
§14.22 Graphics
►In the graphics shown in this section, height corresponds to the absolute value of the function and color to the phase. … ►12: 14.5 Special Values
13: 14.6 Integer Order
…
►
14.6.5
…
14: 14.2 Differential Equations
…
►Ferrers functions and the associated Legendre functions are related to the Legendre functions by the equations , , , , .
…
►
14.2.8
►
14.2.9
…
15: 14.7 Integer Degree and Order
…
►
14.7.6
…
16: 14.15 Uniform Asymptotic Approximations
17: Bibliography O
…
►
Associated Legendre functions on the cut.
J. Comput. Phys. 51 (3), pp. 502–518.
…