Hurwitz zeta function
(0.004 seconds)
1—10 of 19 matching pages
1: 25.11 Hurwitz Zeta Function
§25.11 Hurwitz Zeta Function
►§25.11(i) Definition
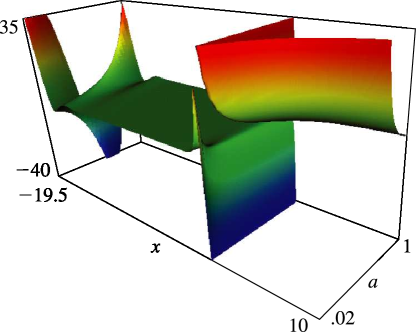
… ►§25.11(ii) Graphics
►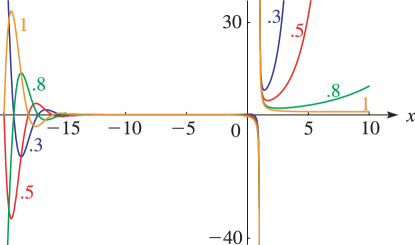 ►
►
2: 25.1 Special Notation
…
►The main related functions are the Hurwitz zeta function
, the dilogarithm , the polylogarithm (also known as Jonquière’s function
), Lerch’s transcendent , and the Dirichlet -functions
.
3: 25.13 Periodic Zeta Function
4: 25.18 Methods of Computation
…
►
§25.18(i) Function Values and Derivatives
… ►Calculations relating to derivatives of and/or can be found in Apostol (1985a), Choudhury (1995), Miller and Adamchik (1998), and Yeremin et al. (1988). ►For the Hurwitz zeta function see Spanier and Oldham (1987, p. 653) and Coffey (2009). …5: 8.15 Sums
6: 25.19 Tables
…
►
•
►
•
Fletcher et al. (1962, §22.1) lists many sources for earlier tables of for both real and complex . §22.133 gives sources for numerical values of coefficients in the Riemann–Siegel formula, §22.15 describes tables of values of , and §22.17 lists tables for some Dirichlet -functions for real characters. For tables of dilogarithms, polylogarithms, and Clausen’s integral see §§22.84–22.858.
7: 25.14 Lerch’s Transcendent
…
►The Hurwitz zeta function
(§25.11) and the polylogarithm (§25.12(ii)) are special cases:
►
25.14.2
, ,
…
8: 25.21 Software
…
►
§25.21(iv) Hurwitz Zeta Function
…9: 25.15 Dirichlet -functions
…
►
25.15.3
…