functions%20f%28%CF%B5%2C%E2%84%93%3Br%29%2Ch%28%CF%B5%2C%E2%84%93%3Br%29
(0.024 seconds)
11—20 of 999 matching pages
11: 20.2 Definitions and Periodic Properties
…
►
§20.2(i) Fourier Series
… ►§20.2(ii) Periodicity and Quasi-Periodicity
… ►The theta functions are quasi-periodic on the lattice: … ►§20.2(iii) Translation of the Argument by Half-Periods
… ►§20.2(iv) -Zeros
…12: 14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
§14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
►§14.20(i) Definitions and Wronskians
… ► … ►§14.20(ii) Graphics
… ►§14.20(x) Zeros and Integrals
…13: 5.12 Beta Function
§5.12 Beta Function
… ►Euler’s Beta Integral
… ►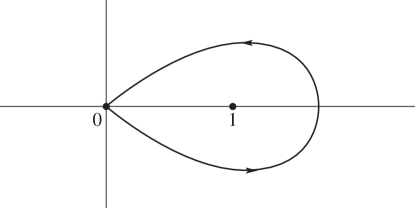 ►
►
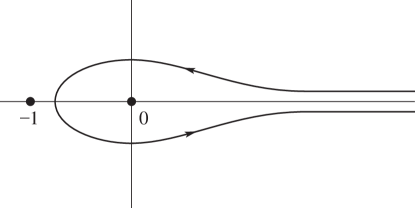 ►
►
Pochhammer’s Integral
…14: 10.1 Special Notation
…
►(For other notation see Notation for the Special Functions.)
…
►The main functions treated in this chapter are the Bessel functions
, ; Hankel functions
, ; modified Bessel functions
, ; spherical Bessel functions
, , , ; modified spherical Bessel functions
, , ; Kelvin functions
, , , .
For the spherical Bessel functions and modified spherical Bessel functions the order is a nonnegative integer.
…For the Kelvin functions the order is always assumed to be real.
…
►For older notations see British Association for the Advancement of Science (1937, pp. xix–xx) and Watson (1944, Chapters 1–3).
15: 4.2 Definitions
16: 8.17 Incomplete Beta Functions
§8.17 Incomplete Beta Functions
… ►§8.17(ii) Hypergeometric Representations
… ►For the hypergeometric function see §15.2(i). ►§8.17(iii) Integral Representation
… ►§8.17(vi) Sums
…17: 1.10 Functions of a Complex Variable
…
►The function
on is said to be analytically continued along the path
, , if there is a chain , .
…
►
§1.10(vi) Multivalued Functions
… ►Let be a multivalued function and be a domain. … ►§1.10(xi) Generating Functions
… ►Then is the generating function for the functions , which will automatically have an integral representation …18: 16.2 Definition and Analytic Properties
…
►
