entire%20functions
(0.003 seconds)
11—20 of 962 matching pages
11: 16.13 Appell Functions
§16.13 Appell Functions
►The following four functions of two real or complex variables and cannot be expressed as a product of two functions, in general, but they satisfy partial differential equations that resemble the hypergeometric differential equation (15.10.1): ►
16.13.1
,
…
►
16.13.4
.
…
►
…
12: 5.12 Beta Function
§5.12 Beta Function
… ►Euler’s Beta Integral
… ►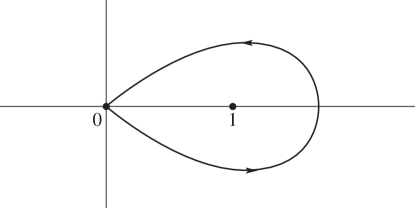 ►
►
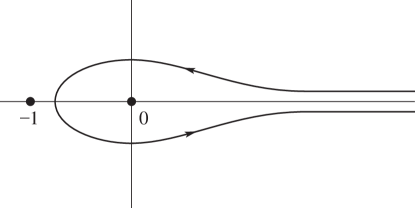 ►
►
Pochhammer’s Integral
…13: 14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
§14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
►§14.20(i) Definitions and Wronskians
… ► … ►§14.20(ii) Graphics
… ►§14.20(x) Zeros and Integrals
…14: 4.2 Definitions
…
►
…
►
§4.2(iii) The Exponential Function
… ►The function is an entire function of , with no real or complex zeros. … ►§4.2(iv) Powers
… ► …15: 10.1 Special Notation
…
►(For other notation see Notation for the Special Functions.)
…
►For the spherical Bessel functions and modified spherical Bessel functions the order is a nonnegative integer.
For the other functions when the order is replaced by , it can be any integer.
For the Kelvin functions the order is always assumed to be real.
…
►For older notations see British Association for the Advancement of Science (1937, pp. xix–xx) and Watson (1944, Chapters 1–3).
16: 16.2 Definition and Analytic Properties
…
►
§16.2(i) Generalized Hypergeometric Series
… ►When the series (16.2.1) converges for all finite values of and defines an entire function. … ► … ►§16.2(v) Behavior with Respect to Parameters
… ►When and is fixed and not a branch point, any branch of is an entire function of each of the parameters .17: 23.2 Definitions and Periodic Properties
…
►
