Hermite polynomials
(0.007 seconds)
11—20 of 59 matching pages
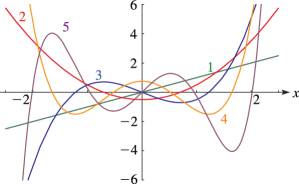
11: 18.4 Graphics
12: 18.5 Explicit Representations
13: 18.11 Relations to Other Functions
14: 18.27 -Hahn Class
15: 18.18 Sums
16: 18.1 Notation
…
►
…
►
►
…
►
►
…
Hermite: , .
Discrete -Hermite I: .
Discrete -Hermite II: .
Continuous -Hermite: .
Continuous -Hermite: