Poisson%20kernel
(0.002 seconds)
11—20 of 134 matching pages
11: 1.8 Fourier Series
12: Bibliography H
…
►
Asymptotic expansion of a class of integral transforms with algebraically dominated kernels.
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 35 (2), pp. 405–433.
…
►
Solutions of Poisson’s equation in channel-like geometries.
Comput. Phys. Comm. 115 (1), pp. 45–68.
…
13: 19.18 Derivatives and Differential Equations
…
►and also a system of
Euler–Poisson differential equations (of which only are independent):
…
►The next four differential equations apply to the complete case of and in the form (see (19.16.20) and (19.16.23)).
►The function satisfies an Euler–Poisson–Darboux equation:
…
14: 18.12 Generating Functions
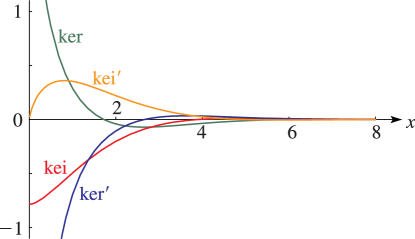
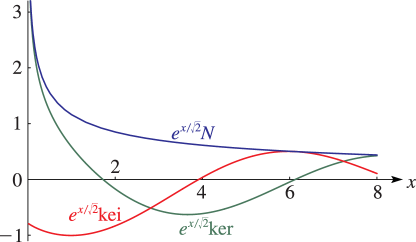
15: 10.62 Graphs
16: 10.61 Definitions and Basic Properties
…
►When suffices on , , , and are usually suppressed.
►Most properties of , , , and follow straightforwardly from the above definitions and results given in preceding sections of this chapter.
…
►
►
…
►
…
17: 8 Incomplete Gamma and Related
Functions
…
18: 28 Mathieu Functions and Hill’s Equation
…
19: 31.10 Integral Equations and Representations
…
►
Kernel Functions
… ►The kernel must satisfy … ►Kernel Functions
… ►The kernel must satisfy … ►leads to the kernel equation …20: 10.67 Asymptotic Expansions for Large Argument
…
►
§10.67(i) , and Derivatives
… ►
10.67.1
…
►The contributions of the terms in , , , and on the right-hand sides of (10.67.3), (10.67.4), (10.67.7), and (10.67.8) are exponentially small compared with the other terms, and hence can be neglected in the sense of Poincaré asymptotic expansions (§2.1(iii)).
…
►
10.67.14
►
10.67.15
…