Eisenstein convention
(0.001 seconds)
11—20 of 24 matching pages
11: Bibliography W
…
►
Elliptic Functions According to Eisenstein and Kronecker.
Classics in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
…
12: Guide to Searching the DLMF
…
►
►
…
$ |
stands for any number of alphanumeric characters |
|---|---|
(the more conventional * is reserved for the multiplication operator) |
|
| … | |
13: 18.20 Hahn Class: Explicit Representations
…
►Here we use as convention for (16.2.1) with , , and that the summation on the right-hand side ends at .
…
14: 16.11 Asymptotic Expansions
15: 18.26 Wilson Class: Continued
…
►Here we use as convention for (16.2.1) with , , and that the summation on the right-hand side ends at .
…
16: 18.21 Hahn Class: Interrelations
…
►
►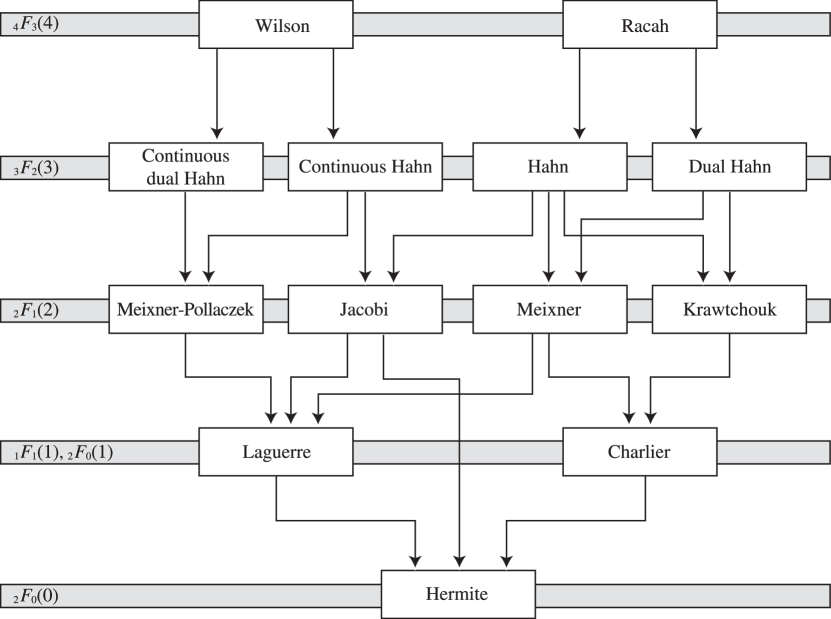 ►
►
Figure 18.21.1: Askey scheme.
…(This is with the convention that the real and imaginary parts of the parameters are counted separately in the case of the continuous Hahn polynomials.)
Magnify
 ►
►
17: 22.2 Definitions
…
►with the convention that functions with the same two letters are replaced by unity; e.
…
18: 4.2 Definitions
…
►With this convention,
…
19: 13.4 Integral Representations
…
►Similar conventions also apply to the remaining integrals in this subsection.
…
