3F2 functions of matrix argument
(0.004 seconds)
11—20 of 982 matching pages
11: 11.9 Lommel Functions
§11.9 Lommel Functions
… ►Provided that , (11.9.1) has the general solution … ►When , … ►§11.9(iii) Asymptotic Expansion
… ►For further information on Lommel functions see Watson (1944, §§10.7–10.75) and Babister (1967, Chapter 3). …12: 16.13 Appell Functions
§16.13 Appell Functions
►The following four functions of two real or complex variables and cannot be expressed as a product of two functions, in general, but they satisfy partial differential equations that resemble the hypergeometric differential equation (15.10.1): ►
16.13.1
,
…
►
16.13.3
,
…
►
…
13: 14.19 Toroidal (or Ring) Functions
§14.19 Toroidal (or Ring) Functions
►§14.19(i) Introduction
… ►§14.19(ii) Hypergeometric Representations
… ►§14.19(iv) Sums
… ►§14.19(v) Whipple’s Formula for Toroidal Functions
…14: 5.15 Polygamma Functions
§5.15 Polygamma Functions
►The functions , , are called the polygamma functions. In particular, is the trigamma function; , , are the tetra-, penta-, and hexagamma functions respectively. Most properties of these functions follow straightforwardly by differentiation of properties of the psi function. … ►In (5.15.2)–(5.15.7) , and for see §25.6(i). …15: 14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
§14.20 Conical (or Mehler) Functions
… ► … ► exists except when and ; compare §14.3(i). … ►For extensions to complex arguments (including the range ), asymptotic expansions, and explicit error bounds, see Dunster (1991). For the case of purely imaginary order and argument see Dunster (2013). …16: 5.2 Definitions
…
►
§5.2(i) Gamma and Psi Functions
►Euler’s Integral
… ►It is a meromorphic function with no zeros, and with simple poles of residue at . … ►
5.2.2
.
…
►
5.2.3
…
17: 31.1 Special Notation
…
►(For other notation see Notation for the Special Functions.)
►
►
►The main functions treated in this chapter are , , , and the polynomial .
…Sometimes the parameters are suppressed.
| , | real variables. |
|---|---|
| … | |
18: 15.2 Definitions and Analytical Properties
…
►
§15.2(i) Gauss Series
►The hypergeometric function is defined by the Gauss series … … ►On the circle of convergence, , the Gauss series: … ►§15.2(ii) Analytic Properties
…19: 5.12 Beta Function
§5.12 Beta Function
… ►Euler’s Beta Integral
… ►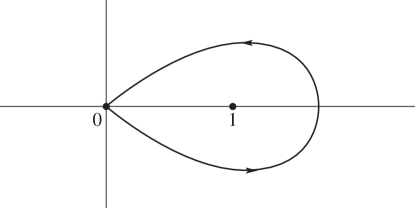 ►
►
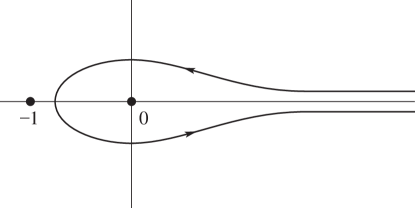 ►
►
Pochhammer’s Integral
…20: 10.1 Special Notation
…
►(For other notation see Notation for the Special Functions.)
…
►For the spherical Bessel functions and modified spherical Bessel functions the order is a nonnegative integer.
For the other functions when the order is replaced by , it can be any integer.
For the Kelvin functions the order is always assumed to be real.
…
►For older notations see British Association for the Advancement of Science (1937, pp. xix–xx) and Watson (1944, Chapters 1–3).
