Toda equation
(0.001 seconds)
11—20 of 450 matching pages
11: 31.13 Asymptotic Approximations
§31.13 Asymptotic Approximations
… ►For asymptotic approximations of the solutions of Heun’s equation (31.2.1) when two singularities are close together, see Lay and Slavyanov (1999). ►For asymptotic approximations of the solutions of confluent forms of Heun’s equation in the neighborhood of irregular singularities, see Komarov et al. (1976), Ronveaux (1995, Parts B,C,D,E), Bogush and Otchik (1997), Slavyanov and Veshev (1997), and Lay et al. (1998).12: 29.19 Physical Applications
…
►
§29.19(ii) Lamé Polynomials
►Ward (1987) computes finite-gap potentials associated with the periodic Korteweg–de Vries equation. …Hargrave (1978) studies high frequency solutions of the delta wing equation. …Roper (1951) solves the linearized supersonic flow equations. Clarkson (1991) solves nonlinear evolution equations. …13: 32.13 Reductions of Partial Differential Equations
§32.13 Reductions of Partial Differential Equations
… ►Equation (32.13.3) also has the similarity reduction … ►§32.13(ii) Sine-Gordon Equation
… ►§32.13(iii) Boussinesq Equation
… ►14: 31.12 Confluent Forms of Heun’s Equation
…
►
Confluent Heun Equation
… ►Doubly-Confluent Heun Equation
… ►Biconfluent Heun Equation
… ►Triconfluent Heun Equation
… ►15: 29.11 Lamé Wave Equation
§29.11 Lamé Wave Equation
►The Lamé (or ellipsoidal) wave equation is given by …In the case , (29.11.1) reduces to Lamé’s equation (29.2.1). …16: 9.16 Physical Applications
…
►A quite different application is made in the study of the diffraction of sound pulses by a circular cylinder (Friedlander (1958)).
…
►In the study of the stability of a two-dimensional viscous fluid, the flow is governed by the Orr–Sommerfeld equation (a fourth-order differential equation).
…An application of Airy functions to the solution of this equation is given in Gramtcheff (1981).
►Airy functions play a prominent role in problems defined by nonlinear wave equations.
These first appeared in connection with the equation governing the evolution of long shallow water waves of permanent form, generally called solitons, and are predicted by the Korteweg–de Vries (KdV) equation (a third-order nonlinear partial differential equation).
…
17: Sidebar 21.SB2: A two-phase solution of the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation (21.9.3)
Sidebar 21.SB2: A two-phase solution of the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation (21.9.3)
… ►A two-phase solution of the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation (21.9.3). …18: 32.12 Asymptotic Approximations for Complex Variables
…
►
§32.12(i) First Painlevé Equation
… ►§32.12(ii) Second Painlevé Equation
… ►§32.12(iii) Third Painlevé Equation
…19: 28.17 Stability as
§28.17 Stability as
… ► ►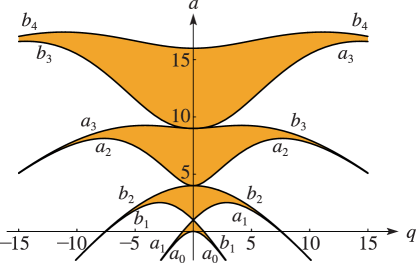 ►
►
