functions s(ϵ,ℓ;r),c(ϵ,ℓ;r)
(0.020 seconds)
1—10 of 570 matching pages
1: 7.2 Definitions
…
►
7.2.8
►
, , and are entire functions of , as are and in the next subsection.
…
►
7.2.10
►
7.2.11
…
2: 22.16 Related Functions
…
►
§22.16(ii) Jacobi’s Epsilon Function
►Integral Representations
… ►Relation to Theta Functions
… ►§22.16(iii) Jacobi’s Zeta Function
►Definition
…3: 28.2 Definitions and Basic Properties
…
►
►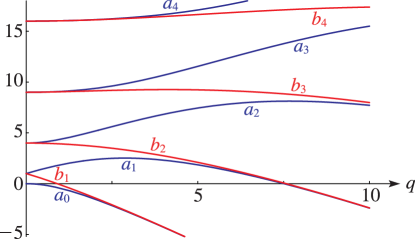 ►
►
Figure 28.2.1: Eigenvalues , of Mathieu’s equation as functions of for , (’s), (’s).
Magnify
…
►
§28.2(ii) Basic Solutions ,
… ►§28.2(iv) Floquet Solutions
… ►
28.2.18
…
►
 ►
►
§28.2(vi) Eigenfunctions
…4: 28.20 Definitions and Basic Properties
5: 19.2 Definitions
…
►Let be a cubic or quartic polynomial in with simple zeros, and let be a rational function of and containing at least one odd power of .
…
►
19.2.1
…
►
19.2.2
…
►
19.2.17
…
►
19.2.21
…
6: 25.1 Special Notation
…
►The main function treated in this chapter is the Riemann zeta function
.
…
►The main related functions are the Hurwitz zeta function
, the dilogarithm , the polylogarithm (also known as Jonquière’s function
), Lerch’s transcendent , and the Dirichlet -functions
.
7: 31.6 Path-Multiplicative Solutions
8: 4.44 Other Applications
…
►The Einstein functions and Planck’s radiation function are elementary combinations of exponentials, or exponentials and logarithms.
…
9: 31.4 Solutions Analytic at Two Singularities: Heun Functions
…
►To emphasize this property this set of functions is denoted by
►
31.4.1
.
…
►
31.4.3
,
…
►The set depends on the choice of and .
…
10: 31.1 Special Notation
…
►The main functions treated in this chapter are , , , and the polynomial .
…Sometimes the parameters are suppressed.
