elementary%20identities
♦
3 matching pages ♦
(0.001 seconds)
3 matching pages
1: 25.5 Integral Representations
2: 25.12 Polylogarithms
…
►
► ►
►
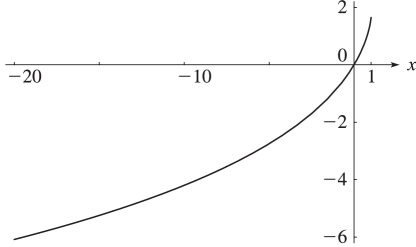
Figure 25.12.1: Dilogarithm function ,
Magnify
►
►
►
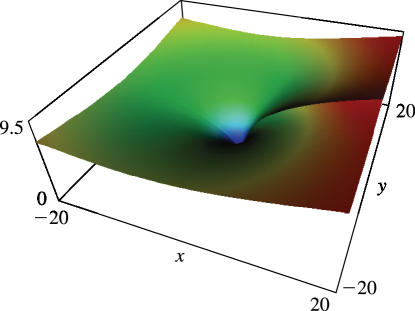
Figure 25.12.2: Absolute value of the dilogarithm function , , .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
►
25.12.1
.
…
►The cosine series in (25.12.7) has the elementary sum
…
►
 ►
►
25.12.11
…
3: Bibliography M
…
►
Spherical Harmonics. An Elementary Treatise on Harmonic Functions with Applications.
3rd edition, International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 98, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
…
►
On the interval computation of elementary functions.
C. R. Acad. Bulgare Sci. 34 (3), pp. 319–322.
…
►
The computation of elementary functions in radix
.
Computing 53 (3-4), pp. 219–232.
…
►
An elementary proof of the Macdonald identities for
.
Adv. in Math. 57 (1), pp. 34–70.
…
►
Elementary Functions: Algorithms and Implementation.
Birkhäuser Boston Inc., Boston, MA.
…