beta function
(0.008 seconds)
1—10 of 179 matching pages
1: 5.12 Beta Function
§5.12 Beta Function
… ►Euler’s Beta Integral
… ►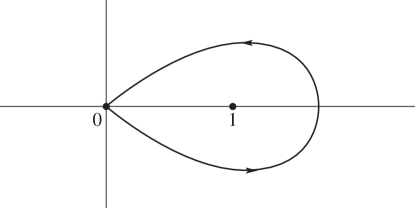 ►
►
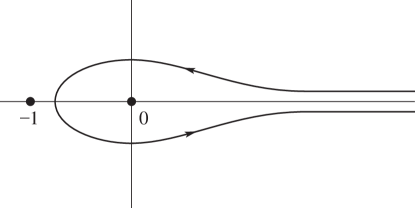 ►
►
Pochhammer’s Integral
…2: 8.17 Incomplete Beta Functions
§8.17 Incomplete Beta Functions
… ►§8.17(ii) Hypergeometric Representations
… ►§8.17(iii) Integral Representation
… ►§8.17(iv) Recurrence Relations
… ►§8.17(vi) Sums
…3: 8.23 Statistical Applications
§8.23 Statistical Applications
… ►The function and its normalization play a similar role in statistics in connection with the beta distribution; see Johnson et al. (1995, pp. 210–275). …4: 8.24 Physical Applications
5: 5.20 Physical Applications
§5.20 Physical Applications
… ►Then the partition function (with ) is given by … ►Elementary Particles
►Veneziano (1968) identifies relationships between particle scattering amplitudes described by the beta function, an important early development in string theory. …6: 8.26 Tables
…
►
§8.26(iii) Incomplete Beta Functions
…7: 5.18 -Gamma and -Beta Functions
8: 35.3 Multivariate Gamma and Beta Functions
9: 8.18 Asymptotic Expansions of
10: 8.1 Special Notation
…
►Unless otherwise indicated, primes denote derivatives with respect to the argument.
►The functions treated in this chapter are the incomplete gamma functions
, , , , and ; the incomplete beta functions
and ; the generalized exponential integral ; the generalized sine and cosine integrals , , , and .
►Alternative notations include: Prym’s functions
, , Nielsen (1906a, pp. 25–26), Batchelder (1967, p. 63); , , Dingle (1973); , , Magnus et al. (1966); , , Luke (1975).
