Hankel
(0.001 seconds)
11—20 of 73 matching pages
11: 10.3 Graphics
…
►
►
►
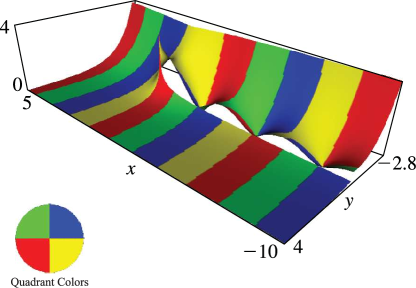
Figure 10.3.10:
, , .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
►
►
►
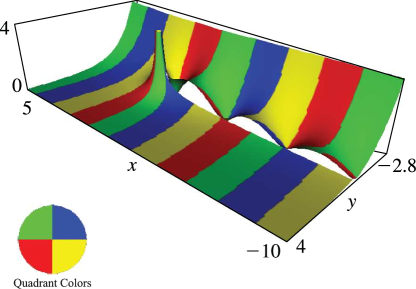
Figure 10.3.12:
, , .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
►
►
►
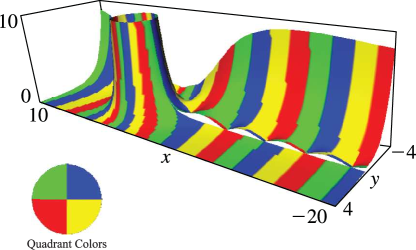
Figure 10.3.14:
, , .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
►
►
►
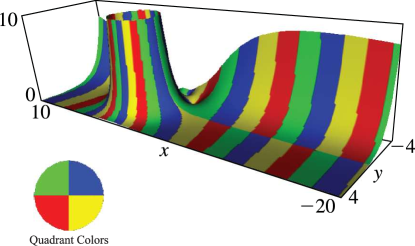
Figure 10.3.16:
, , .
…
Magnify
3D
Help
…
§10.3(ii) Real Order, Complex Variable
… ►12: 10.8 Power Series
§10.8 Power Series
… ►When is not an integer the corresponding expansions for , , and are obtained by combining (10.2.2) with (10.2.3), (10.4.7), and (10.4.8). … ►The corresponding results for and are obtained via (10.4.3) with . …13: 11.1 Special Notation
14: 10.17 Asymptotic Expansions for Large Argument
…
►
§10.17(i) Hankel’s Expansions
… ► … ►§10.17(iii) Error Bounds for Real Argument and Order
… ►§10.17(v) Exponentially-Improved Expansions
… ►For higher re-expansions of the remainder terms see Olde Daalhuis and Olver (1995a) and Olde Daalhuis (1995, 1996).15: 10.76 Approximations
…
►
§10.76(ii) Bessel Functions, Hankel Functions, and Modified Bessel Functions
…16: 10.74 Methods of Computation
…
►For evaluation of the Hankel functions and for complex values of and based on the integral representations (10.9.18) see Remenets (1973).
…
►
►
§10.74(vi) Zeros and Associated Values
… ►Hankel Transform
… ►The spherical Bessel transform is the Hankel transform (10.22.76) in the case when is half an odd positive integer. …17: 10.19 Asymptotic Expansions for Large Order
§10.19 Asymptotic Expansions for Large Order
►§10.19(i) Asymptotic Forms
… ►
10.19.2
…
►
§10.19(iii) Transition Region
… ►See also §10.20(i).18: 10.27 Connection Formulas
19: 10.50 Wronskians and Cross-Products
…
►
…