Dedekind%20sums
(0.002 seconds)
1—10 of 429 matching pages
1: 27.14 Unrestricted Partitions
…
►and is a Dedekind sum given by
…
►
§27.14(iv) Relation to Modular Functions
►Dedekind sums occur in the transformation theory of the Dedekind modular function , defined by …where and is given by (27.14.11). ►For further properties of the function see §§23.15–23.19. …2: 23.17 Elementary Properties
3: 23.18 Modular Transformations
…
►
Dedekind’s Eta Function
►
23.18.5
…
►
23.18.7
.
►Here is a Dedekind sum.
…Note that is of level .
…
4: 23.16 Graphics
…
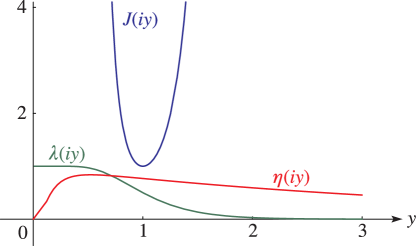
►See Figures 23.16.1–23.16.3 for the modular functions , , and .
…
►
► ►
►
Figure 23.16.1: Modular functions , , for .
…
Magnify
…
►
►
►
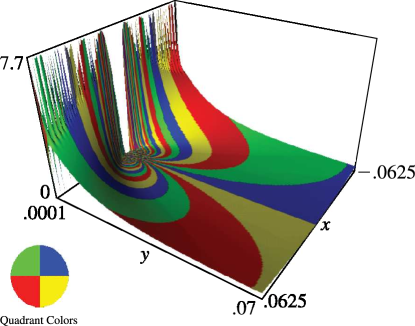
Figure 23.16.3: Dedekind’s eta function for , .
Magnify
3D
Help
 ►
►
5: 23.19 Interrelations
6: 23.15 Definitions
7: Bibliography R
…
►
On the definition and properties of generalized - symbols.
J. Math. Phys. 20 (12), pp. 2398–2415.
…
►
Infinite Sum of the Incomplete Gamma Function Expressed in Terms of the Hurwitz Zeta Function.
Mathematics 9 (16).
…
►
Another proof of the triple sum formula for Wigner -symbols.
J. Math. Phys. 40 (12), pp. 6689–6691.
…
►
Finite-sum rules for Macdonald’s functions and Hankel’s symbols.
Integral Transform. Spec. Funct. 10 (2), pp. 115–124.
…
►
Elliptic and modular functions from Gauss to Dedekind to Hecke.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
…
8: Ranjan Roy
…
►He also authored another two advanced mathematics books: Sources in the development of mathematics (Roy, 2011), Elliptic and modular functions from Gauss to Dedekind to Hecke (Roy, 2017).
…
9: Bibliography
…
►
Exact linearization of a Painlevé transcendent.
Phys. Rev. Lett. 38 (20), pp. 1103–1106.
…
►
On the degrees of irreducible factors of higher order Bernoulli polynomials.
Acta Arith. 62 (4), pp. 329–342.
…
►
Repeated integrals and derivatives of Bessel functions.
SIAM J. Math. Anal. 20 (1), pp. 169–175.
…
►
Theorems on generalized Dedekind sums.
Pacific J. Math. 2 (1), pp. 1–9.
…
►
Bernoulli’s power-sum formulas revisited.
Math. Gaz. 90 (518), pp. 276–279.
…
10: 23.1 Special Notation
…
►The main functions treated in this chapter are the Weierstrass -function ; the Weierstrass zeta function ; the Weierstrass sigma function ; the elliptic modular function ; Klein’s complete invariant ; Dedekind’s eta function .
…