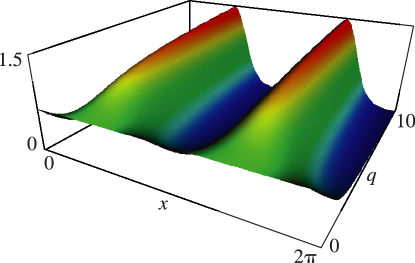
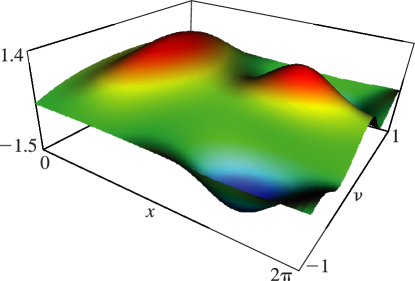
…
► For another listing of Web-accessible software for the functions in this chapter, see
GAMS (class C3 ) .
…
…
►
28.11.1
f
(
z
)
=
α
0
ce
0
(
z
,
q
)
+
∑
n
=
1
∞
(
α
n
ce
n
(
z
,
q
)
+
β
n
se
n
(
z
,
q
)
)
,
…
►
α
n
=
1
π
∫
0
2
π
f
(
x
)
ce
n
(
x
,
q
)
d
x
,
…
►
28.11.3
1
=
2
∑
n
=
0
∞
A
0
2
n
(
q
)
ce
2
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
►
28.11.4
cos
2
m
z
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
A
2
m
2
n
(
q
)
ce
2
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
m
≠
0
,
►
28.11.5
cos
(
2
m
+
1
)
z
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
A
2
m
+
1
2
n
+
1
(
q
)
ce
2
n
+
1
(
z
,
q
)
,
…
…
► For real
q
each of the functions
ce
2
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
se
2
n
+
1
(
z
,
q
)
,
ce
2
n
+
1
(
z
,
q
)
, and
se
2
n
+
2
(
z
,
q
)
has exactly
n
zeros in
0
<
z
<
1
2
π
.
…For
q
→
∞
the zeros of
ce
2
n
(
z
,
q
)
and
se
2
n
+
1
(
z
,
q
)
approach asymptotically the zeros of
𝐻𝑒
2
n
(
q
1
/
4
(
π
−
2
z
)
)
, and the zeros of
ce
2
n
+
1
(
z
,
q
)
and
se
2
n
+
2
(
z
,
q
)
approach asymptotically the zeros of
𝐻𝑒
2
n
+
1
(
q
1
/
4
(
π
−
2
z
)
)
.
…Furthermore, for
q
>
0
ce
m
(
z
,
q
)
and
se
m
(
z
,
q
)
also have purely imaginary zeros that correspond uniquely to the purely imaginary
z
-zeros of
J
m
(
2
q
cos
z
)
(§
10.21(i) ), and they are asymptotically equal as
q
→
0
and
|
ℑ
z
|
→
∞
.
…
…
►
►
ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
se
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
fe
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
ge
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
me
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
►
…
►
►
Ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
Se
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
Fe
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
Ge
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
…
►
…
►
in
n
=
fe
n
,
ceh
n
=
Ce
n
,
inh
n
=
Fe
n
,
…
►
Se
n
(
s
,
z
)
=
ce
n
(
z
,
q
)
ce
n
(
0
,
q
)
,
…
►
Se
n
(
c
,
z
)
=
ce
n
(
z
,
q
)
ce
n
(
0
,
q
)
,
…
…
►
28.5.8
𝒲
{
ce
n
,
fe
n
}
=
ce
n
(
0
,
q
)
fe
n
′
(
0
,
q
)
,
…
► For further information on
C
n
(
q
)
,
S
n
(
q
)
, and expansions of
f
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
g
n
(
z
,
q
)
in Fourier series or in series of
ce
n
,
se
n
functions, see
McLachlan (1947 , Chapter VII) or
Meixner and Schäfke (1954 , §2.72) .
…
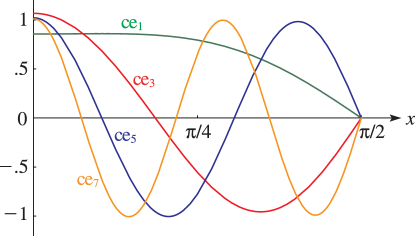
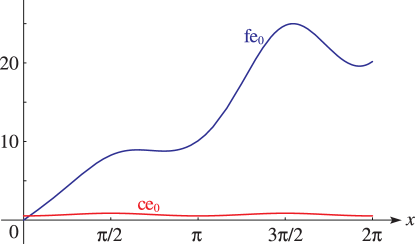
►
► ►
Figure 28.5.1:
fe
0
(
x
,
0.5
)
for
0
≤
x
≤
2
π
and (for comparison)
ce
0
(
x
,
0.5
)
.
Magnify
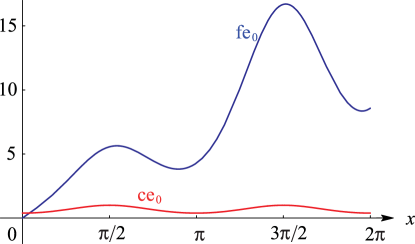
►
► ►
Figure 28.5.2:
fe
0
(
x
,
1
)
for
0
≤
x
≤
2
π
and (for comparison)
ce
0
(
x
,
1
)
.
Magnify
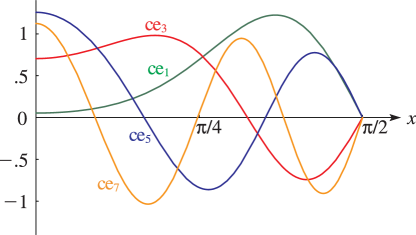
►
► ►
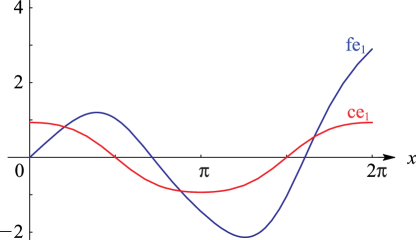
Figure 28.5.3:
fe
1
(
x
,
0.5
)
for
0
≤
x
≤
2
π
and (for comparison)
ce
1
(
x
,
0.5
)
.
Magnify
…
…
►
28.22.1
Mc
m
(
1
)
(
z
,
h
)
=
2
π
1
g
e
,
m
(
h
)
ce
m
(
0
,
h
2
)
Ce
m
(
z
,
h
2
)
,
…
►
28.22.3
Mc
m
(
2
)
(
z
,
h
)
=
2
π
1
g
e
,
m
(
h
)
ce
m
(
0
,
h
2
)
(
−
f
e
,
m
(
h
)
Ce
m
(
z
,
h
2
)
+
2
π
C
m
(
h
2
)
Fe
m
(
z
,
h
2
)
)
,
…
►
28.22.5
g
e
,
2
m
(
h
)
=
(
−
1
)
m
2
π
ce
2
m
(
1
2
π
,
h
2
)
A
0
2
m
(
h
2
)
,
►
28.22.6
g
e
,
2
m
+
1
(
h
)
=
(
−
1
)
m
+
1
2
π
ce
2
m
+
1
′
(
1
2
π
,
h
2
)
h
A
1
2
m
+
1
(
h
2
)
,
…
►
fe
m
′
(
0
,
h
2
)
=
1
2
π
C
m
(
h
2
)
(
g
e
,
m
(
h
)
)
2
ce
m
(
0
,
h
2
)
,
…
…
►
me
n
(
z
,
q
)
=
2
ce
n
(
z
,
q
)
,
n
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
…
,
…
►
§28.12(iii) Functions
ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
se
ν
(
z
,
q
)
, when
ν
∉
ℤ
►
28.12.12
ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
=
1
2
(
me
ν
(
z
,
q
)
+
me
ν
(
−
z
,
q
)
)
,
…
►
28.12.14
ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
=
ce
ν
(
−
z
,
q
)
=
ce
−
ν
(
z
,
q
)
,
…
► Again, the limiting values of
ce
ν
(
z
,
q
)
and
se
ν
(
z
,
q
)
as
ν
→
n
(
≠
0
)
are
not the functions
ce
n
(
z
,
q
)
and
se
n
(
z
,
q
)
defined in §
28.2(vi) .
…
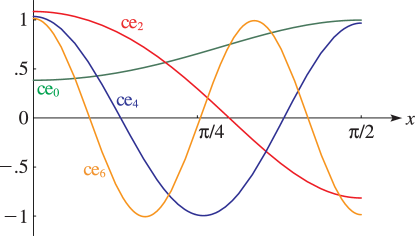 ►
►
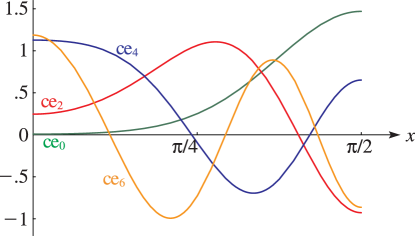 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►
 ►
►